The Skills of Tomorrow
The field of Human Resource Management (HRM) is constantly evolving and therefore identifying key skills for the future workforce has become crucial. In recent years, the (r)evolution of entire industries has taken place, supported by disruptive technological advances such as automation, artificial intelligence, COVID-19 and increasing globalisation. As a result, companies and professionals must consider what the essential and most effective skills of the future will be. Answering this question is highly important, especially considering that it is directly linked to the success of organisations.
The Skills Evolution - How it started

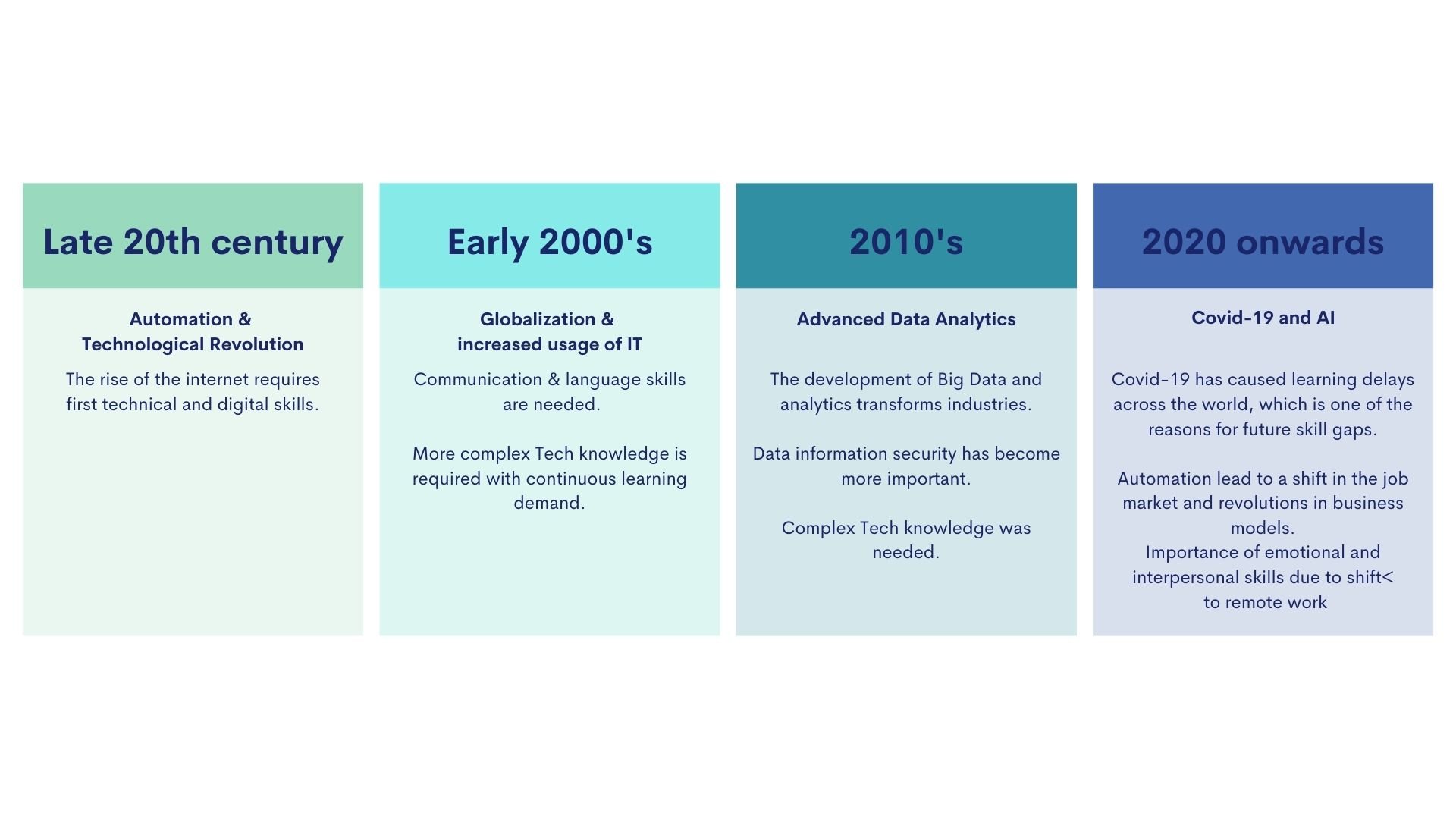
With the rise of the digital age in the late 20th century, technology evolved rapidly. Compact computers enabled the ownership of portable devices, while the Internet's emergence impacted both businesses and individuals. This revolution necessitated a substantial skill shift, especially in technical and digital competencies, for success in this new environment.
The early 2000s were a crucial moment when globalisation and rapid technological advances reshaped the business landscape. Borders blurred, creating a more interconnected world where international connections became a critical success factor, increasing the importance of language & intercultural skills. In the meantime, the digital revolution has led to an increase in the need for more complex technical skills. Programming, networking and software skills became essential as organisations sought to adapt to the evolving digital environment.
Then, about ten years later, advanced data analytics became the key driver for success and the development of big data and analytics revolutionised industries. This change also led to a greater emphasis on data security for both legal and natural persons, leading to an increased demand for even more advanced technical knowledge and experts in data security.
Since 2020, COVID-19 and increasing automation have profoundly changed our lives, especially with the widespread adoption of remote working across all industries. This change emphasises the importance of digital collaboration tools and platforms for the coordination of remote teams, which require appropriate skills. As automation reshapes the labour market, human skills such as emotional intelligence and interpersonal skills are becoming increasingly important, especially in remote work. This was visible at the beginning of the pandemic when the importance of empathy, adaptability and effective communication to get through uncertain times became clear.
.jpg?width=832&height=468&name=Automation%20and%20artificial%20intelligence%20will%20accelerate%20the%20shift%20in%20skills%20that%20the%20workforce%20needs.%20(2).jpg)
In line with socio-cultural, socio-economic and technological changes, the skills required will continue to change in the future. You can find out how the required skills are currently forecast in the course of the article.
What is the current status?
The data indicates the urgent need for proactive actions, not just in offering employees opportunities but also in guiding them through the changes and ensuring they perceive them as opportunities rather than threats.
- 50% of all employees will need a reskilling by 2025
- 300m jobs could be substituted by GenAI worldwide
- 43% of the EU population leaked in digital skills already pre-pandemic
- 50% of employees agree that automation gives them the chance to develop their skills
- 30% think that automation reduces the available job opportunities
What skills will be needed in the future and what skills will become obsolete?
As a result of globalisation, demographic shifts and technology, the workplace has been reshaped, and individuals and organisations must adapt to remain competitive in an uncertain and challenging environment. These skill gaps are already visible, following a study from McKinsey, 87% of companies worldwide are experiencing already skill gaps or expect them within the next 5 years.
The following chart shows which skills will become more relevant and which will be less relevant in the future.
.jpg?width=1920&height=1080&name=Automation%20and%20artificial%20intelligence%20will%20accelerate%20the%20shift%20in%20skills%20that%20the%20workforce%20needs.%20(1).jpg)
As visible in the graph, physical & manual skills as well as basic cognitive skills will become less relevant by 2030 whereas higher cognitive, social & emotional and technological skills will become more important.
The reduction in hours spent on physical, manual, and basic cognitive tasks will necessitate workers to deepen their existing knowledge or acquire new skill sets. While the demand for certain professions won’t decline, the shift will occur due to the increasing automation of work activities that can be automated. Consequently, the need for both basic and advanced technological skills will rise. Individuals who grasp current and future technologies, coupled with the ability to innovate and develop, will be highly valued. Although this won’t apply to the majority, the importance of everyone acquiring at least basic digital and technological skills will become increasingly evident by 2030 and beyond.
As machines advance, it’s evident that they cannot fully replace humans in every aspect. Specifically, social and emotional skills—such as empathy, effective communication, and leadership—will play a crucial role in fostering positive international collaborations, maintaining healthy company cultures, and achieving success in the future. Additionally, there will be a shift from basic cognitive skills (which can be automated) to higher-order cognitive abilities like critical thinking, creativity, and decision-making.
Talking about Tech more in concrete...
We have just seen that technical skills will become highly relevant in the future, but what are the emerging Tech-fields within the next years:- Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML) & Data Science: Reflecting on the previous sections, it's not surprising that AI, ML & Data Science play a relevant role in both our professional and personal lives. As we look towards the future, these technologies will continue to gain relevance because of their abilities to automate tasks, analyze complex data sets, draw conclusions and personalize various business sectors such as Marketing & Customer Service. Furthermore, they facilitate process optimisation and research, demonstrating their versatility and impact on the evolving technology and business landscape.
- Software Development: It encompasses front-end, back-end, and full-stack development, among other aspects, serving as the core of companies' digital transformation. Software development not only drives innovation within businesses but also elevates customer satisfaction, boosts operational effectiveness, drives economic progress, and ultimately enables competitive advantages. Due to this variety, SD will become increasingly important for companies in the future. Furthermore, will AI copilots and No Code/Low Code platforms become even more relevant, as they democratize Software Development, allowing more people and different roles within companies to participate in development processes. These tools simplify complex tasks, making it easier for non-developers to contribute to software projects, thereby accelerating digital transformation and fostering a more inclusive approach to innovation and problem-solving.
- Cyber security: The rise of Automation & AI brings opportunities, but also significant risks that cannot be ignored. Cyber threats have become more advanced and frequent, making further investigation into cybersecurity needed. These risks not only affect individuals and businesses but also extend to national security concerns. As our digital footprint expands, the potential for attacks grows wider, underscoring the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures. Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the transition to remote work, offering flexibility and scalability to organizations. However, these advancements also introduce new security challenges, including the need to secure remote access, safeguard cloud infrastructure, and mitigate risks associated with third-party providers.
Besides technical skills, what are the top skills for 2030?
- Critical thinking: In times when fake news appears more, critical thinking is the most important talent to have for success. Thinking critically is evaluating events and problems in light of the available facts rather than speculation, bias, or hearsay. By using critical thinking techniques, one can determine what is true and false in a range of circumstances and challenges given information.
- Creativity: It can be defined as "the process of transforming imaginative concepts into tangible reality". In the future workplace, creativity will be prized, especially as routine tasks become automated. Key creative thinking abilities like brainstorming, problem-solving, thinking innovatively, and implementing ideas for enhancement will be indispensable in tomorrow's professional environment.
- Collaboration: As teams adapt to incorporate hybrid workers, fully remote employees, contractors, and individuals transitioning between projects and teams, the dynamics of collaboration and teamwork are evolving. In this shifting professional landscape, mastering the art of effective collaboration and communication with diverse colleagues and coworkers will be crucial.
- Flexibility: In the workplace of the future, change will be an even bigger driving force than today. It will be essential to develop the mental resilience to thrive in times of constant change. Adaptable people are open-minded, curious and willing to learn new things because they focus on opportunities rather than obstacles.
- Leadership Skills: Leaders are a crucial factor when talking about a team's performance as it can bring out the best, but also the negative in team members. Factors such as distributed teams, increasing diversity and more fluid organisational structures mean that leadership skills are important for everyone in the company, regardless of the team's responsibility.
- Time management: In times of distributed teams and flexible working agreements, having time management skills without being constantly supervised will become more important. This does not only apply to the company's good but also to oneself.
-
Curiosity and Continuous Learning: Maintaining curiosity and a commitment to continuous learning not only keeps employees adaptable and open to change but also sharpens their ability to navigate today's ever-evolving landscape. With all mentioned above, it's necessary to have this open and positive mindset towards what's yet to come.
Why should organisations invest in these skills?

How to successfully bridge the skills gap?
As discussed earlier, the skills needed today may not suffice for the future. Companies must invest in developing and empowering their workforce with the necessary skills or hiring individuals who already possess them. By engaging in development initiatives, employees have the opportunity to bridge any skill gaps they may have. This can involve acquiring new skills, known as reskilling, or enhancing existing ones and gaining additional knowledge relevant to their current role, referred to as upskilling.
The graphic below explains the difference between Reskilling & Upskilling, the purpose and the advantages. Depending on the job, the company and the future need either one of the other is the appropriate solution.
Sources: Agrawal et al. (2020), beyondbots, Bughin et al. (2018), Bruggs et al. (2023), McKinsey (2023), Mouddene et al.(2018) Whiting (2020)


-1.png)